
Introduction
Snake bites can be a cause of concern and fear for many people. While most snakes are harmless and play a vital role in maintaining ecological balance, some venomous snakes pose a threat to humans. This article aims to provide an overview of snake bites, including prevention, identification, and treatment.

Snake Bite Identification
It is crucial to identify whether a snake bite is venomous or non-venomous. Venomous snake bites often leave two distinct puncture marks, while non-venomous snake bites usually have a single row of teeth marks. Additionally, venomous snake bites tend to cause immediate pain, swelling, and discoloration around the bite area.
Preventing Snake Bites
Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to snake bites. By taking simple precautions, you can reduce the risk of encountering venomous snakes. Avoid walking barefoot in areas with dense vegetation, wear protective clothing such as boots and long pants, and be cautious when handling rocks or logs where snakes may hide.

What to Do If Bitten
If you or someone you know is bitten by a snake, it is essential to remain calm and take immediate action. First, move away from the snake to prevent further bites. Keep the bitten limb immobilized and at the level of the heart. It is crucial not to panic and seek medical help as soon as possible.

Do's and Don'ts
When dealing with snake bites, it is important to remember a few do's and don'ts. Do try to remember the snake's appearance or take a picture if possible, as it can help with identification. Don't apply a tourniquet or ice to the bite area, as these methods are no longer recommended and can worsen the situation.
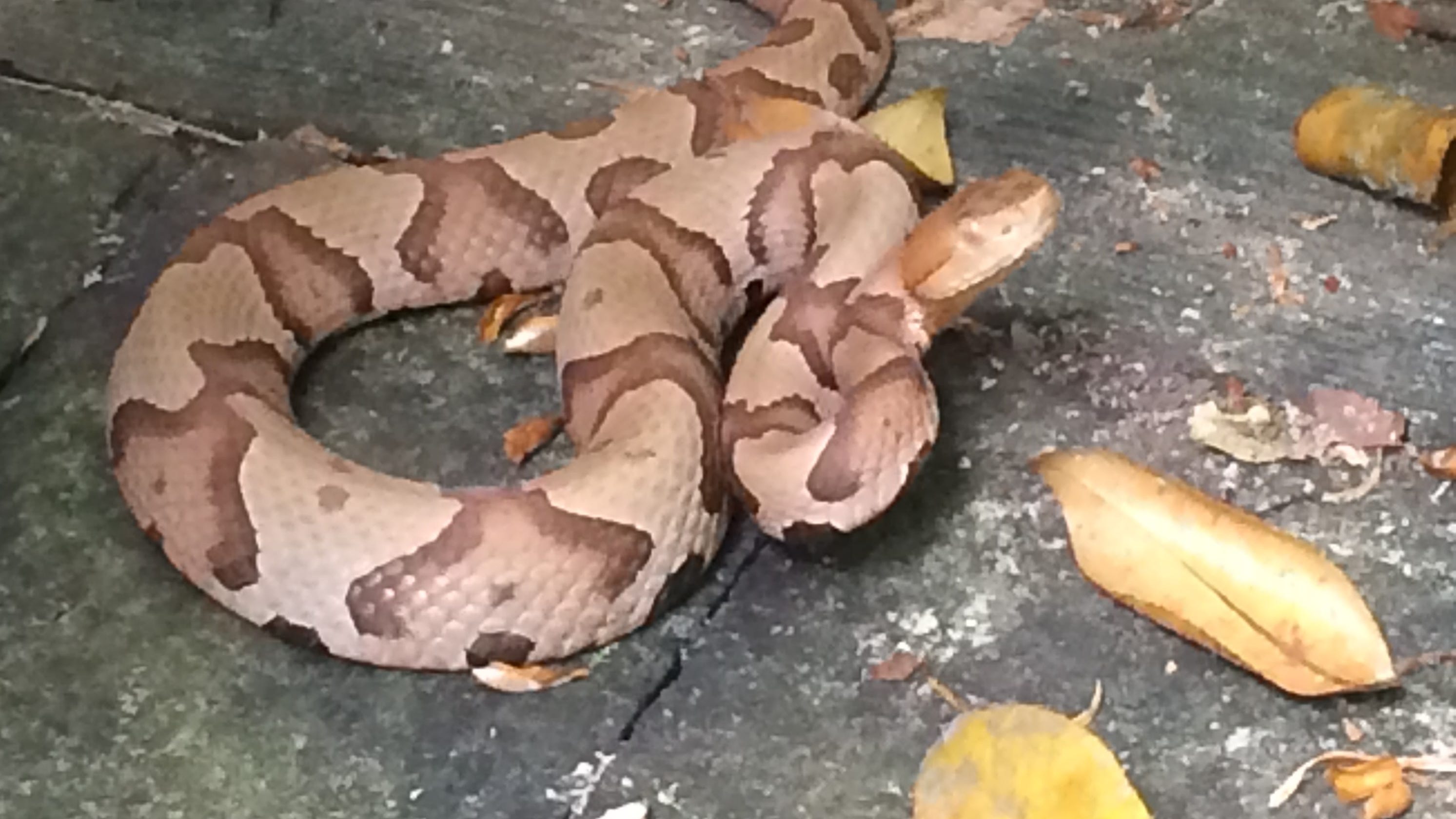

Types of Venomous Snakes
Various species of venomous snakes exist worldwide, each with its distinct characteristics and venom composition. Some common venomous snakes include the rattlesnake, copperhead, cottonmouth, and coral snake. Knowing the types of venomous snakes in your region can help in understanding the potential risks.

Snake Bite First Aid
Providing appropriate first aid for snake bites is crucial before reaching a medical facility. Keep the bitten person calm and still, and remove any constrictive clothing or jewelry near the bite site. Clean the wound with mild soap and water, and cover it with a clean, sterile dressing.
Common Snake Bite Symptoms
Snake bite symptoms can vary depending on the species and amount of venom injected. Common symptoms include localized pain, swelling, redness, and bruising around the bite site. Other symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, dizziness, difficulty breathing, and changes in heart rate.

Snake Bite Treatment
Proper medical treatment is crucial for snake bite victims. Antivenom is typically administered to neutralize the snake's venom. The specific antivenom depends on the snake species and the region. Other treatments may include pain management, wound care, and monitoring for potential complications.

Complications and Long-Term Effects
Snake bites can lead to various complications and long-term effects, especially if not promptly treated. These may include infection, tissue damage, allergic reactions, and even psychological trauma. It is essential to receive appropriate medical care and follow-up to minimize potential complications.

Snake Bite Myths
Snake bites have been surrounded by numerous myths and misconceptions. It is crucial to dispel these myths to ensure accurate knowledge and appropriate actions. Some common snake bite myths include sucking out the venom, cutting the wound, or using traditional remedies, which are ineffective and potentially harmful.

Snake Bite Statistics
Understanding snake bite statistics provides valuable insights into the prevalence and impact of snake bites globally. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), it is estimated that snake bites result in tens of thousands of deaths and disabilities each year, predominantly affecting rural populations in tropical and subtropical regions.
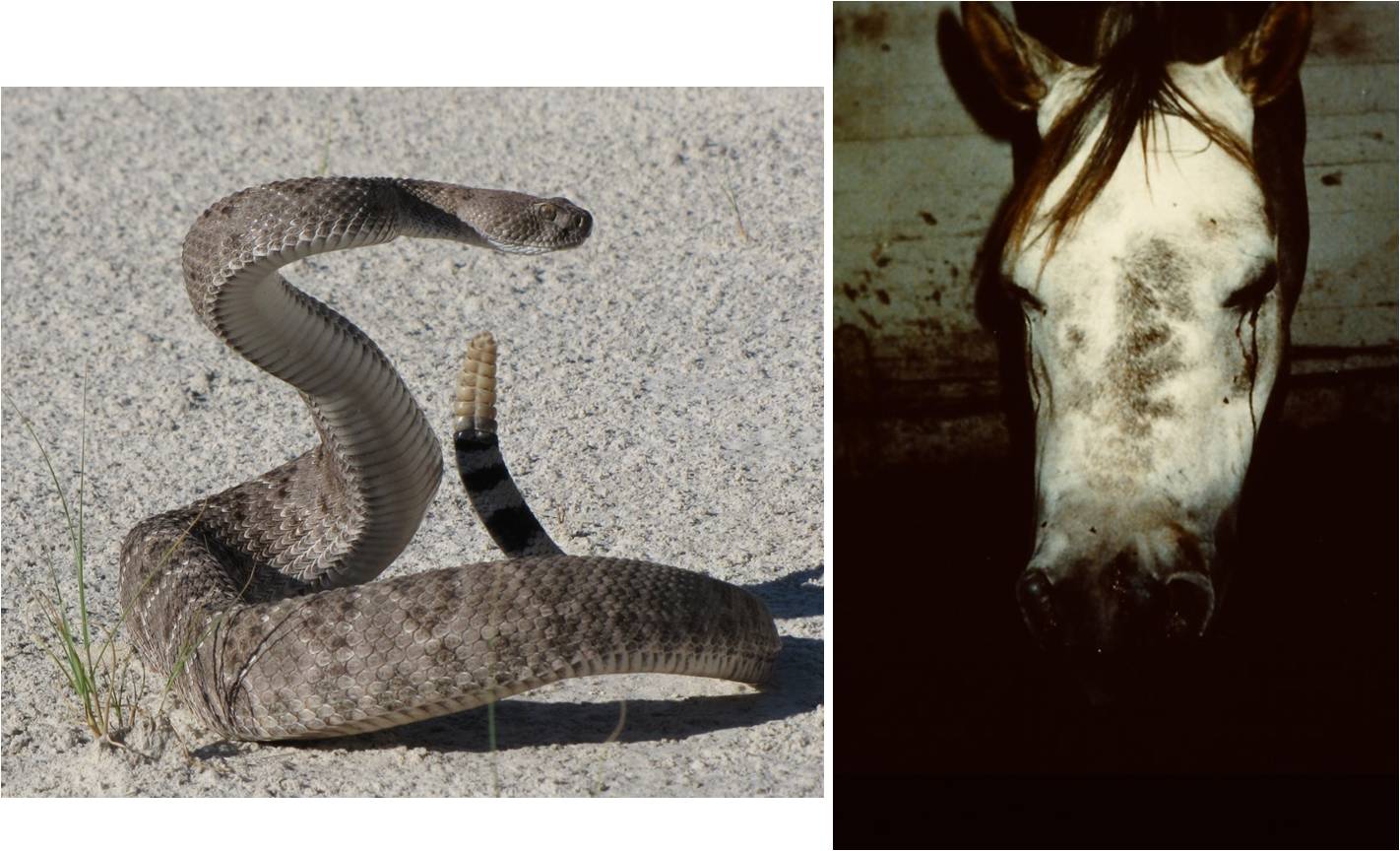

Snake Bite Prevention Tips
Prevention is key when it comes to snake bites. Here are some additional tips to help you stay safe:
- Avoid walking in tall grass or areas with low visibility.
- Be cautious when stepping over logs, rocks, or fallen trees.
- Use a flashlight when moving around in the dark, especially outdoors.
- Keep your living areas clean and free of clutter, as snakes may seek shelter in piles of debris.
- Teach children about the potential dangers of snakes and how to react appropriately if they encounter one.
Conclusion
Snake bites can be a serious medical emergency, but with proper understanding, prevention, and prompt treatment, the risks can be minimized. By following the guidelines mentioned in this article, you can enhance your knowledge about snake bites and take appropriate measures to protect yourself and others.