Introduction
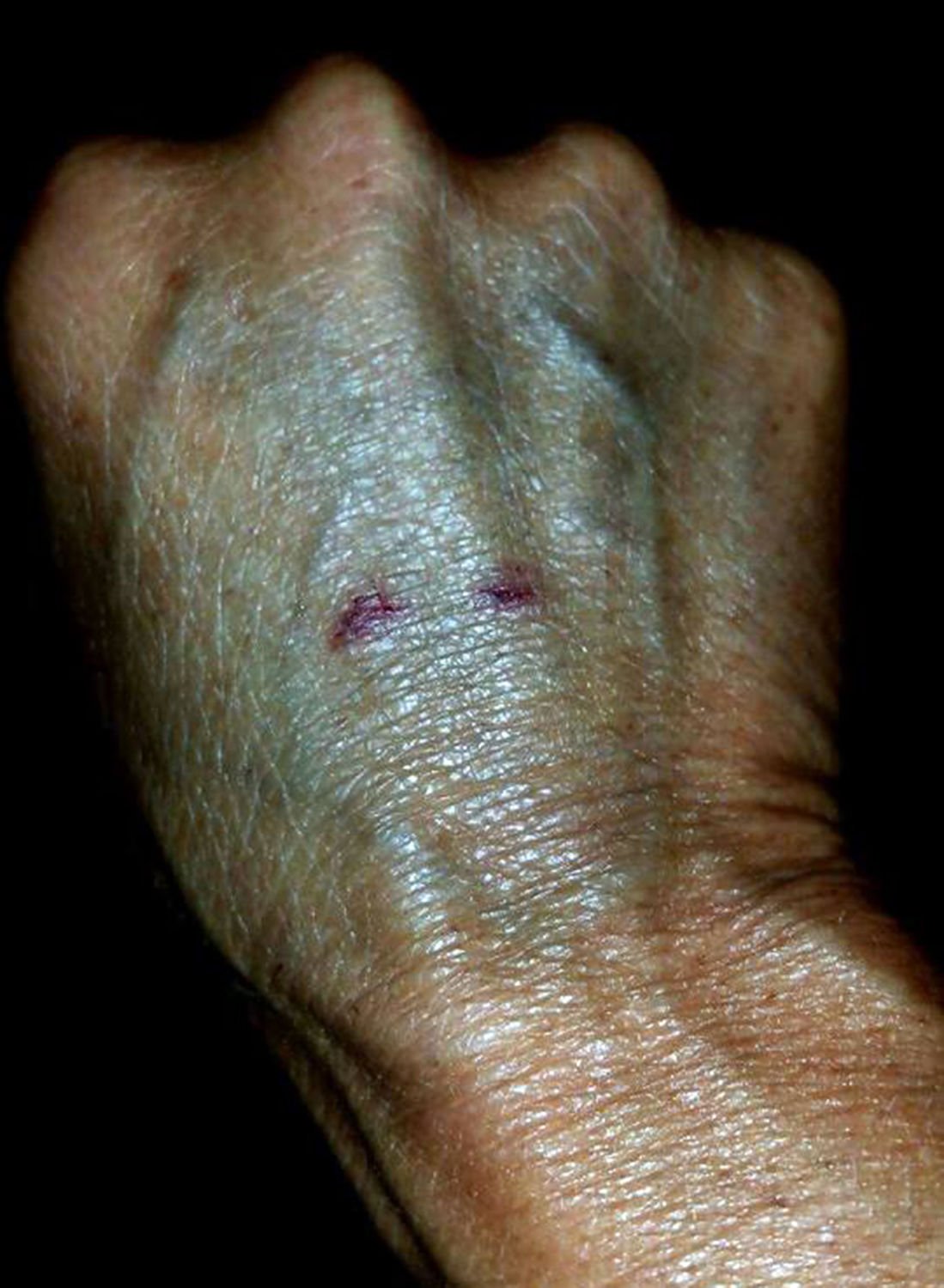
A snake bite occurs when a snake injects venom into a person's body through its fangs. Snake bites can be a serious and life-threatening emergency, requiring immediate medical attention. It is important to understand the types of snakes, their venom, and the steps to take after a snake bite to ensure the best possible outcome.
Types of Venomous Snakes

There are numerous venomous snake species around the world. Some common venomous snakes include the rattlesnake, copperhead, cottonmouth, coral snake, and various species of cobras, vipers, and mambas. Each snake possesses unique venom with varying effects on the human body.
Symptoms of a Snake Bite

The symptoms of a snake bite can vary depending on the snake species and the amount of venom injected. Common symptoms include localized pain, swelling, redness, and bleeding. More severe symptoms may include difficulty breathing, dizziness, nausea, muscle weakness, and even paralysis.
First Aid for Snake Bites

When someone is bitten by a snake, it is crucial to act quickly and provide appropriate first aid before seeking medical help. Here are the steps to take:
1. Stay calm and reassure the victim.
2. Keep the affected limb immobilized and lower than the heart level.
3. Remove any constrictive items like jewelry or tight clothing from the affected area.
4. Clean the bite wound gently with soap and water if available.
5. Apply a sterile bandage or dressing to cover the wound.
6. Do not apply a tourniquet or attempt to suck out the venom.
7. Transport the victim to the nearest medical facility as soon as possible.
Treatment for Snake Bites

Upon reaching a medical facility, healthcare professionals will assess the snake bite and administer appropriate treatment. This may involve:
1. Administering antivenom specific to the snake species.
2. Monitoring vital signs and providing supportive care.
3. Managing pain and reducing swelling with medications.
4. Tetanus vaccination if needed.
5. Conducting blood tests to assess the impact of venom on the body.
6. Performing any necessary surgical procedures, such as debridement or fasciotomy.
Preventing Snake Bites

Prevention is key to avoiding snake bites. Here are some preventive measures:
1. Wear appropriate footwear and clothing when in snake-prone areas.
2. Stay on designated paths and avoid tall grass or bushes.
3. Avoid reaching into dark or hidden areas without proper visibility.
4. Be cautious when handling logs, rocks, or debris where snakes may hide.
5. Do not provoke or handle snakes, even if they appear non-threatening.
6. Educate yourself and others about local snake species and their habitats.
Conclusion
Snake bites can be dangerous, but prompt medical attention and proper first aid can significantly improve the outcome. By staying calm, following preventive measures, and seeking immediate medical help, the risk of complications from snake bites can be minimized.